 25
Oct,2025
25
Oct,2025
Ergonomic Chair Risk Calculator
Assess Your Chair Setup Risk
Risk Assessment
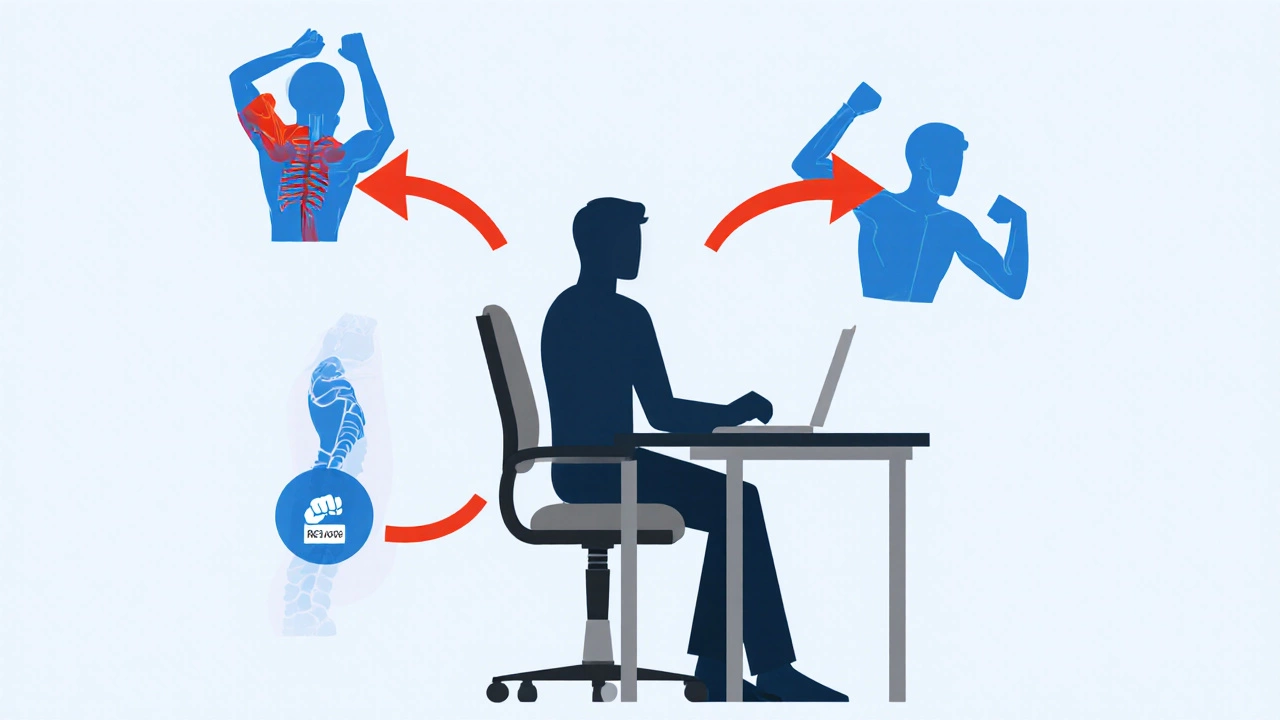
When you sit in a Chair without armrests is a type of office seating that lacks the side supports most ergonomic chairs provide. Without those supports, the body must compensate in ways that can strain muscles, reduce focus, and even lead to long‑term injury. In this guide we’ll break down exactly what goes wrong, why it matters for productivity, and how you can fix it without spending a fortune.
What Happens to Your Body?
Removing armrests forces your shoulders, neck, and upper back to work harder. Here are the main physiological effects:
- Shoulder elevation: Your arms hover, causing the trapezius muscles to stay contracted.
- Wrist deviation: Without a surface to rest on, wrist angle often shifts outward, increasing strain on the carpal tunnel.
- Spinal tilt: To keep the forearms stable you may lean forward, flattening the natural lumbar curve.
Over time those micro‑movements add up to Repetitive strain injury (RSI) a group of musculoskeletal disorders caused by repetitive motions or sustained awkward positions, which can manifest as neck pain, shoulder tension, or numbness in the hands.
How It Affects Your Work
Imagine typing for eight hours with your elbows floating in mid‑air. Your muscles fatigue faster, which leads to frequent breaks, lower focus, and slower task completion. Studies from occupational health labs show a 12‑15% dip in typing speed when workers use chairs lacking arm support.
Beyond raw speed, the mental toll is real. Discomfort triggers cortisol spikes, making you feel stressed and less creative. In fast‑paced office environments, those small losses compound into missed deadlines.
Key Ergonomic Elements That Miss Armrests
Armrests interact with several other ergonomic features. Let’s look at them one by one:
- Ergonomic armrest a padded extension that supports the forearm and helps maintain a neutral shoulder posture. This component distributes the weight of the arms and reduces shoulder shrugging.
- Lumbar support a curvature or adjustable pad that preserves the natural inward curve of the lower spine. Without armrests, users often lean forward, negating the benefit of lumbar support.
- Desk height the vertical distance between the floor and the work surface, critical for aligning elbows with the keyboard. If the desk is too high, armrests become essential for keeping elbows close to the body.
- Posture the alignment of the spine, shoulders, and hips while seated. Armrests encourage a relaxed, upright posture.
- Keyboard and mouse positioning the placement of input devices within easy reach, ideally at elbow height. Without arm support, reaching for the mouse can cause shoulder rotation.
The interplay of these elements means that lacking one (armrests) can undermine the others.
When Might a Chair Without Armrests Be Acceptable?
There are a few niche scenarios where you can get away without armrests:
- Short‑term tasks: If you only sit for 30‑minute intervals, the strain is minimal.
- Space‑constrained desks: Some compact workstations leave no room for side supports.
- Dynamic work styles: Standing‑desk users who switch between sitting and standing may prefer a minimalist seat.
Even in those cases, adding a separate forearm cushion or an ergonomic keyboard tray can help bridge the gap.
Choosing the Right Chair: A Quick Checklist
| Feature | With Armrests | Without Armrests |
|---|---|---|
| Shoulder Load | Low - support distributes weight | High - shoulders lift |
| Wrist Angle | Neutral - forearms rest | Potential deviation |
| Posture Stability | Better - reduces forward lean | Reduced - more slouching |
| Cost | Typically $150‑$400 | $80‑$200 |
| Adjustability | Height, width, pivot | Often limited |
Use this table as a starting point when shopping. If the price difference is small, always opt for the version with adjustable armrests.
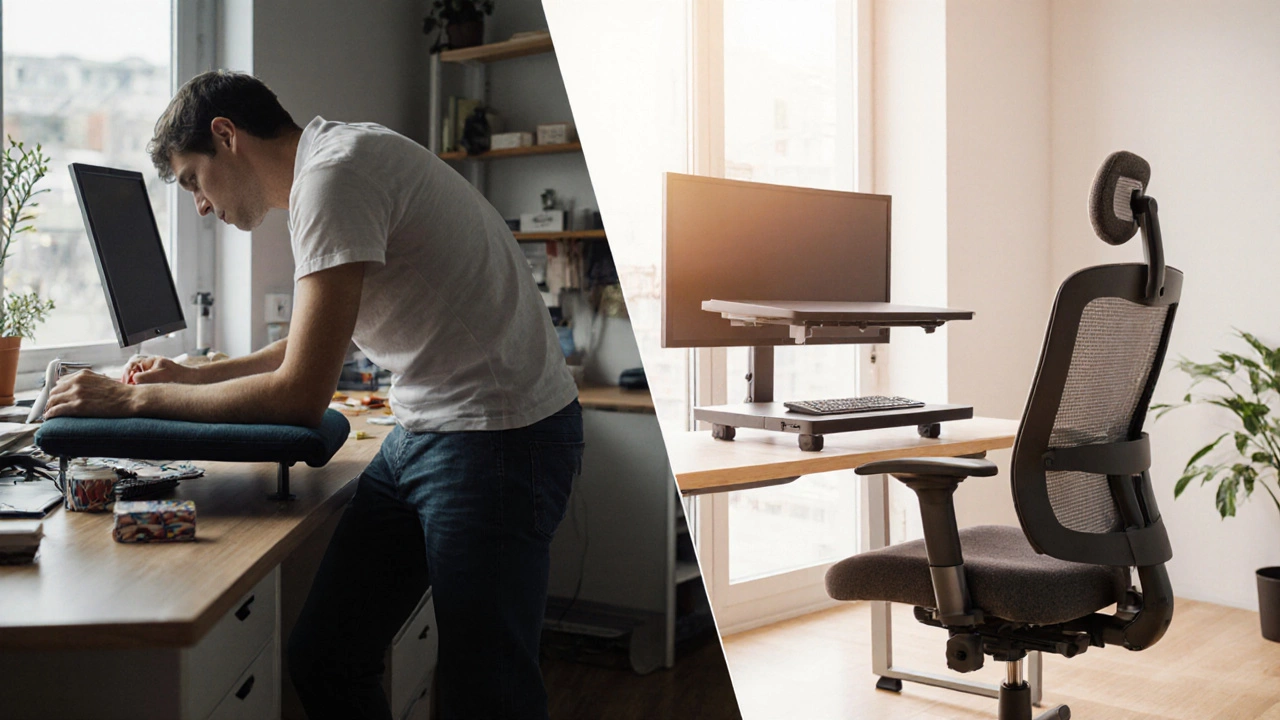
Simple Fixes If You’re Stuck With a No‑Armrest Chair
Don’t panic if you already own a chair that lacks side supports. Here are five low‑cost tweaks:
- Place a forearm cushion a small padded pad that rests on the desk to support the forearms at the edge of your desk.
- Adjust desk height so elbows sit at a 90‑degree angle while typing.
- Use a monitor riser a stand that lifts the screen to eye level, reducing neck strain and allowing shoulders to relax.
- Take micro‑breaks every 45‑60 minutes: stand, stretch, roll shoulders.
- Consider an adjustable chair a seat with height, tilt, and lumbar adjustments that can compensate for missing armrests if you plan a future upgrade.
These steps won’t turn a bad chair into a perfect one, but they dramatically lower the risk of pain and fatigue.
Putting It All Together
In short, a chair without armrests forces the body to work harder, which can lead to shoulder tension, wrist strain, and reduced productivity. The good news is that the problem is easy to identify and even easier to fix-whether by choosing a better chair, adding simple accessories, or tweaking your desk setup.
Next time you shop for office furniture, ask yourself: "Do the armrests support a neutral posture?" If the answer is no, you’ve just spotted a hidden cost.
Why do armrests matter for back health?
Armrests keep the shoulders relaxed and maintain the natural curve of the spine. When they’re missing, the upper back and neck often compensate, leading to chronic tension and reduced lumbar support effectiveness.

Can a forearm cushion replace armrests?
A forearm cushion helps reduce wrist deviation, but it doesn’t provide the same shoulder support that true armrests do. It’s a good temporary fix, especially for tight desks, but not a full substitute.
How often should I take breaks to avoid strain?
Aim for a 1‑2 minute micro‑break every 45‑60 minutes. Stand, stretch the shoulders, and roll the neck. Over the course of a day this adds up to less fatigue and lower risk of RSI.
Is a cheaper chair without armrests worth it for a home office?
If you only work short bursts or have an adjustable desk that lets you stand often, the cost savings might make sense. Otherwise, investing a little more for armrests pays off in comfort and long‑term health.
What other chair features should I look for besides armrests?
Key features include adjustable lumbar support, seat depth, synchro‑tilt mechanism, and breathable mesh back. Together they create a balanced ergonomic system that works even if you occasionally sit without armrests.




